This 30 Second Technique is Shockingly Effective
The Impact of Conductive Hearing Loss on Communication and How to Overcome It
Understanding Conductive Hearing Loss
There are various forms of hearing loss and distinguishing among them is key. Conductive hearing loss occurs when there's a blockage or an issue with sound waves being transmitted through the outer ear, eardrum, or middle ear. If you're struggling to follow conversations or consistently turning up the volume on your television, you might be experiencing this condition.
What is Conductive Hearing Loss?
When sound cannot efficiently travel from the outside world to the inner ear, you might be dealing with conductive hearing loss. This condition is not due to problems with the sensory cells or nerve pathways but rather stems from physical issues in the ear's pathway for sound.
Causes Behind Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss can stem from a variety of issues, ranging from simple to complex. Common causes include ear infections, excessive earwax, fluid in the middle ear due to colds or allergies, perforated eardrums, benign tumors, or structural anomalies in the ear canal or issues with the Eustachian tube.
Determining Conductive Hearing Loss
A thorough evaluation, including a review of one's medical history, a physical examination, and specialized hearing tests, is fundamental to diagnosing this auditory disorder. Tests like tympanometry can assess the function of the middle ear, while pure tone audiometry can determine the degree and specific type of hearing loss.
The Process of Conductive Hearing Loss
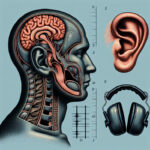
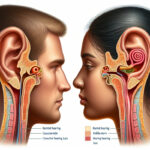
Understanding how sound is normally conducted helps to comprehend how conductive hearing loss happens. Sound travels through the air, enters the outer ear, and reaches the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations are then transmitted to the inner ear by the ossicles in the middle ear.
Normal Sound Transmission
In an unaffected ear, sound waves travel into the ear canal, causing the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then amplified by the small bones of the middle ear, the ossicles, and sent to the cochlea, where they are transformed into electrical signals for the brain to interpret.
Interruptions in Sound Transmission
In cases of conductive hearing loss, there are disruptions in this system. Blockages from earwax or dampening of sound vibrations due to fluid in the middle ear are examples of how this transmission can be interrupted.
The Role of the Middle Ear in Hearing
The middle ear acts as an amplifier and a bridge between the outer and inner ear. If there's damage to the ossicles or infections are present, this amplification and transmission process is compromised, resulting in conductive hearing loss.
Differentiating Conductive Hearing Loss From Other Auditory Disorders
Conductive hearing loss differs from other types of auditory challenges, each with its own set of issues for those affected. It's important to recognize these differences for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Sensorineural Versus Conductive Hearing Loss
Unlike conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss is due to damage to the hair cells in the cochlea or the auditory nerve and is often permanent. On the other hand, conductive hearing loss may be temporary and treatable with medical or surgical interventions.
Understanding Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural issues, affecting both the transmission of sound to the cochlea and the cochlea or auditory nerve itself, thereby complicating treatment.
Unique Challenges of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss can present unique challenges, such as the risk of misdiagnosis or overlooking symptoms due to their variability. The impact on quality of life can be significant, but with the right treatment, it is manageable.
Impact of Conductive Hearing Loss on Daily Conversation
Communication is a cornerstone of human interaction, and any hindrance can have broad repercussions. While often manageable, conductive hearing loss can significantly affect everyday communication.
Difficulty in Speech Comprehension
Individuals with conductive hearing loss may find it hard to understand speech, especially in noisy environments. This can lead to frequent misunderstandings and the need to ask for repetition, resulting in frustration for both parties in the conversation.
Social and Emotional Effects
Communication difficulties may lead to social isolation, increased anxiety, and depression. The extra effort needed to follow conversations can make social interactions exhausting, causing some to avoid these situations altogether.
Implications for Professional and Academic Life
Conductive hearing loss can also impact performance at work or in school. Challenges in catching every word spoken can lead to missed information and misunderstandings, negatively affecting collaboration and learning.
Tips for Communicating with Conductive Hearing Loss
Despite the challenges, there are methods to help navigate the communication barriers posed by conductive hearing loss.
Reading Lips and Recognizing Visual Cues
Lip-reading, along with paying attention to facial expressions and gestures, can provide context clues to aid in understanding spoken language. This visual information can compensate for what is missed auditorily.
Using Assistive Listening Devices
Assistive listening devices, such as amplified phones, FM systems, or personal amplifiers, can enhance the volume and clarity of sound for those with conductive hearing loss, aiding in conversations.
Adapting Communication Techniques
Friends and family can improve communication by facing the individual while speaking, reducing background noise, and speaking clearly without needing to shout. These adjustments can greatly improve the quality of interactions.
Medical and Surgical Remedies
Various medical and surgical treatments are available to address the underlying causes of conductive hearing loss.
Medicinal Treatments
Medications such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs can be effective for conditions related to infections or allergies, potentially restoring normal hearing function.
Surgical Procedures
For structural problems, surgeries like tympanoplasty or ossiculoplasty can correct or replace the problematic elements of the ear, often restoring hearing ability.
The Importance of Timely Treatment
Delaying treatment for conductive hearing loss can lead to worsening of the condition and make future treatment more challenging. Therefore, it's crucial to seek prompt intervention.
Living with Conductive Hearing Loss: Adaptation and Support
Adapting to life with conductive hearing loss is an ongoing process. With adequate resources and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
Exploring Hearing Aids and Other Devices
While hearing aids are commonly used for sensorineural hearing loss, certain types can also benefit those with conductive issues. For instance, bone conduction hearing aids offer a potential solution.
Connecting with Support Groups and Resources
Connecting with others who face similar challenges can offer comfort. Support groups, available in person and online, provide opportunities to share experiences and advice.
Developing a Long-Term Management Plan
Working with audiologists and healthcare professionals to craft a comprehensive management plan can assist individuals with conductive hearing loss in maintaining their hearing health over time.
Future Directions in Conductive Hearing Loss Treatment
Continued research presents an optimistic outlook for individuals with conductive hearing loss.
Advancements in Medical Technology
Progress in medical technology, including improved surgical techniques and innovative hearing devices, is constantly enhancing treatment outcomes and quality of life for those affected by conductive hearing loss.
Potential of Regenerative Medicine
The field of regenerative medicine is forging new paths in the treatment of hearing loss. Studies into stem cell therapy and gene therapy offer the potential for future treatments that could repair or regenerate the ear's damaged structures.
Promoting Advocacy and Increasing Awareness
Increased advocacy and awareness are crucial for ensuring that individuals with conductive hearing loss receive the timely and proper care they need. Advocacy also plays a pivotal role in securing funding for research and the development of new treatment methods.

Laura Henderson is a health enthusiast and has been interested in healthy and natural methods of eliminating tinnitus and restoring natural hearing for many years.