This 30 Second Technique is Shockingly Effective
Decibel Hearing Test Demystified: What to Expect During the Procedure
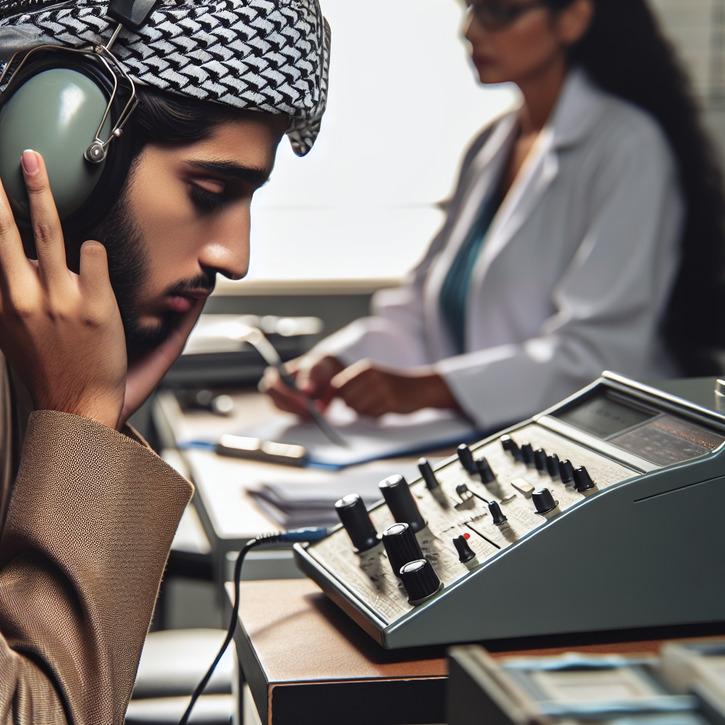

Introduction to Decibel Hearing Tests
Welcome to the world of auditory health, where the decibel hearing test plays a pivotal role in assessing your hearing capabilities. In this guide, we'll demystify the process, from preparation to interpretation of results. Understanding the importance of these assessments is key to maintaining your auditory well-being. Decibels are units of measurement that gauge the intensity of sound, and they are fundamental in quantifying hearing loss. By exploring the procedure of decibel hearing tests, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview and alleviate any concerns you might have about undergoing this important evaluation.
Understanding the Importance of Hearing Assessments
Hearing assessments are crucial for detecting hearing loss early, which can significantly impact your quality of life. Whether it's conversing with loved ones or enjoying the sounds of nature, our hearing connects us to the world. By regularly undergoing decibel hearing tests, you ensure that any changes in your hearing health are promptly addressed. Moreover, these tests can reveal hearing conditions that may require medical attention or the use of hearing aids, making them an indispensable tool in your overall health maintenance routine.
The Role of Decibels in Measuring Hearing Ability
Decibels (dB) serve as the standard unit for measuring sound pressure levels and, by extension, hearing ability. Sounds range from the faintest whisper around 20 dB to the roar of a jet engine above 120 dB. A decibel hearing test evaluates how your ears respond to various decibel levels, helping audiologists determine the softest sounds you can hear at different frequencies. This assessment is vital in understanding the degree to which your hearing may be compromised and in what auditory range.
Overview of the Decibel Hearing Test Procedure
The decibel hearing test, formally known as pure-tone audiometry, involves listening to a series of tones at varying volumes and pitches. These tones are presented through headphones or earplugs connected to an audiometer, which the audiologist controls. You will indicate when you hear each sound, and the audiologist will record these responses. This procedure is painless and non-invasive, providing a clear picture of your hearing thresholds across the frequency spectrum.
Preparing for a Decibel Hearing Test
Preparation is minimal for a decibel hearing test, but a few simple steps can help ensure accurate results. Schedule your test with a certified audiologist or hearing clinic, and make a note of any medications you're currently taking that could affect your hearing. It's also recommended to avoid loud noise exposure for at least 24 hours before the test to prevent temporary threshold shifts that could skew the results. Gather any relevant medical records or previous hearing test results to bring along to your appointment.
Scheduling and What to Bring
When scheduling your decibel hearing test, choose a date and time that allows you to arrive relaxed and prepared. Mornings are often ideal, as you're less likely to be fatigued and can avoid the hustle and bustle of the day. Remember to bring a photo ID, insurance information if applicable, and a list of any hearing-related symptoms or concerns you've experienced. This information will be invaluable to your audiologist in providing a thorough assessment and personalized care.
Avoiding Noise Exposure Before the Test
To ensure your ears are at their baseline state for the test, it's critical to protect them from loud noises beforehand. Prolonged exposure to high-decibel environments can temporarily reduce your hearing sensitivity, leading to inaccurate test results. Use hearing protection when exposed to loud sounds and opt for quieter activities in the day leading up to your test. This simple precaution can make a significant difference in the accuracy of your hearing assessment.
Medications and Health Conditions to Disclose
Some medications and health conditions can affect hearing, so it's important to disclose this information to your audiologist. Certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and even high dosages of aspirin can impact hearing sensitivity. Additionally, if you have a history of ear infections, tinnitus, or any ear surgeries, make sure to inform the specialist conducting the test. A comprehensive health profile allows for a more accurate interpretation of your hearing test results.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Decibel Hearing Test
Upon arriving at the clinic, you'll be greeted by the staff and asked to fill out preliminary paperwork, which may include your medical history, current symptoms, and any specific hearing concerns. This information will guide your audiologist in customizing the test to your needs. You'll then meet with the hearing specialist who will explain the process and answer any questions before beginning the assessment.
Checking in and Preliminary Paperwork
The first step at the clinic involves a straightforward check-in process. You'll provide your personal details and receive paperwork to complete. This typically includes a questionnaire about your hearing health and lifestyle. Be thorough and honest; the more information your audiologist has, the better they can tailor the test and subsequent recommendations to your situation. Once the paperwork is finished, you'll be one step closer to understanding your hearing health.
The Role of an Audiologist or Hearing Specialist
An audiologist or hearing specialist is a trained professional who specializes in identifying, diagnosing, and treating hearing and balance disorders. During the decibel hearing test, they will guide you through the procedure, ensuring you're comfortable and understand each step. Their expertise is not only crucial during the testing phase but also in interpreting the results and recommending appropriate interventions if hearing loss is detected.
The Testing Environment
The environment in which the decibel hearing test is conducted is meticulously crafted to ensure accurate results. You'll be seated in a soundproof booth or a room specifically designed to minimize ambient noise. This controlled setting is essential for eliminating outside sounds that could interfere with the test. Inside this quiet space, you can focus on the sounds presented to you without distraction, allowing for a precise measurement of your hearing thresholds.
Understanding the Testing Equipment
The main piece of equipment used in a decibel hearing test is the audiometer, which generates pure tones at specific frequencies and decibel levels. You'll wear headphones or ear inserts connected to the audiometer, through which the sounds will be played. It's crucial that these headphones fit properly and that you're comfortable, as this will help you focus and respond accurately to the tones.
Types of Headphones Used in Hearing Tests
During a decibel hearing test, you may encounter two types of headphones: supra-aural headphones, which rest on your ears, or insert earphones, which fit snugly inside your ear canals. Each type has its benefits in delivering sound directly to your ears without external noise interference. Your audiologist will choose the best option for you based on the test's requirements and your comfort.
The Audiometer: Key to the Decibel Hearing Test
The audiometer is a sophisticated device that allows the audiologist to control the pitch (frequency) and volume (intensity) of tones during the test. It's capable of producing a wide range of sounds, from very low to very high frequencies, and at varying levels of loudness. The audiologist adjusts these settings to find the threshold at which you can just barely hear the sound, which is recorded as your hearing sensitivity for that frequency.
The Soundproof Testing Booth
The soundproof booth is designed to isolate you from any external noises that could affect the testing process. Constructed with specialized acoustic materials, the booth ensures that the only sounds you hear are those coming through the headphones. This level of sound control is essential in obtaining a clear and accurate assessment of your hearing abilities.
During the Test: What Happens?
Once comfortably seated in the soundproof booth, the audiologist will conduct pure-tone audiometry. You'll hear a series of beeps or tones through the headphones, and you'll be asked to respond—typically by pressing a button or raising your hand—whenever you hear a sound. The tones will vary in pitch and volume, and the audiologist will carefully record the softest level at which you can detect each frequency. This process is methodical and requires your full concentration.
The Pure-Tone Audiometry Process
Pure-tone audiometry is a non-invasive hearing test that measures your ability to hear sounds of specific pitches and volumes. The test begins with tones at a volume you can easily hear, which are gradually decreased until you can no longer detect them. This threshold, the softest sound you can hear 50% of the time, is noted on an audiogram. The process is repeated for various frequencies to map out your hearing ability across the spectrum of pitch.
Threshold Testing for Different Frequencies
Threshold testing is a core component of the decibel hearing test. The audiologist will play tones at different frequencies, starting with the lowest (bass) and moving to the highest (treble) sounds. You'll indicate when you can no longer hear the tone, and these thresholds are recorded. By testing a range of frequencies, the audiologist can identify specific areas of hearing loss, which is essential for understanding how your hearing loss may affect daily life and communication.
Bone Conduction Testing
In addition to the standard air conduction testing, you may undergo bone conduction testing. This involves placing a small device behind your ear to send vibrations directly to the inner ear, bypassing the middle and outer ear. It helps the audiologist determine whether hearing loss is due to problems with sound transmission through the ear canal and middle ear (conductive hearing loss) or with the inner ear or auditory nerve (sensorineural hearing loss).
Interpreting Your Test Results
After completing the decibel hearing test, the audiologist will review and interpret your audiogram, a visual representation of your hearing thresholds. An audiogram plots the softest sounds you can hear at different frequencies and intensities. The results indicate the degree and type of hearing loss you may have, providing a basis for discussing potential treatments or hearing aids if necessary.
Reading the Audiogram
An audiogram is a graph that displays your hearing sensitivity across frequencies and intensities. Frequencies are listed from low to high (left to right), and intensities are listed from soft to loud (top to bottom). Your hearing thresholds are marked on the graph, with a line connecting these points to visualize your hearing profile. Interpreting the audiogram can reveal if you have normal hearing, mild, moderate, severe, or profound hearing loss.
Determining Hearing Loss Levels
Hearing loss levels are determined by the range of decibels at which you can barely detect sound. Normal hearing typically falls between -10 to 20 dB. Mild hearing loss is indicated by thresholds between 21 to 40 dB, moderate from 41 to 55 dB, moderate-severe from 56 to 70 dB, severe from 71 to 90 dB, and profound at 91 dB or more. This categorization helps in deciding the most appropriate intervention, such as hearing aids or cochlear implants.
Discussing Next Steps: Treatment and Management
Once your hearing level is determined, the audiologist will discuss the next steps with you. If hearing loss is present, they may recommend hearing aids, assistive listening devices, or further medical evaluations. Treatment plans are personalized, taking into account your lifestyle, the severity of hearing loss, and your preferences. Proper management and treatment can significantly improve your communication abilities and overall quality of life.
After the Test: FAQs and Common Concerns
Following your decibel hearing test, you may have questions or concerns about your results and what they mean for your future. It's normal to feel anxious, but your audiologist is there to provide support and clear up any confusion. They can walk you through the test outcomes, explain the implications for your hearing health, and discuss any recommended follow-up procedures or hearing protection strategies.
When to Retest: Monitoring Your Hearing Health
Monitoring your hearing health is an ongoing process. Depending on your test results and risk factors for hearing loss, your audiologist will recommend a schedule for retesting. Typically, adults should have their hearing tested every few years, but more frequent testing may be necessary if you're exposed to loud noises regularly or have a history of hearing loss. Staying proactive with retesting can help you maintain optimal hearing health.
Addressing Anxiety About Test Results
It's natural to feel apprehensive about the outcome of your decibel hearing test. However, remember that identifying hearing loss early can lead to more effective management. Approach the results as an opportunity to improve your hearing health, whether that means getting hearing aids, making lifestyle changes, or simply being more aware of your auditory environment. Your audiologist is a valuable resource for support and guidance, whatever the results may be.
Protecting Your Hearing Post-Test
After your decibel hearing test, take steps to protect your hearing regardless of the results. Use ear protection in noisy environments, keep the volume down on personal audio devices, and give your ears regular breaks from sound exposure. If you've been diagnosed with hearing loss, follow your audiologist's recommendations for treatment and hearing aids. Staying vigilant about your auditory health can make a world of difference.
Conclusion: The Importance of Regular Decibel Hearing Tests
Regular decibel hearing tests are a crucial part of maintaining your auditory health. They allow for early detection of hearing loss, which can be key in preventing further deterioration and ensuring effective management. As we've explored, the test is straightforward and painless, and it provides invaluable insights into your hearing capabilities. We encourage you to prioritize these assessments and remain proactive in monitoring and caring for your hearing health.
Summarizing the Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection of hearing loss through decibel hearing tests can have a profound impact on your quality of life. Timely intervention can slow the progression of hearing loss, improve communication, and even prevent related health issues such as cognitive decline. By understanding the benefits of early detection, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your hearing and continue to enjoy the sounds around you.
Encouraging Continued Hearing Health Awareness
Continued awareness of your hearing health is essential. Just as you would attend regular check-ups for your eyes or teeth, your ears deserve the same attention. Stay informed about the risks of noise exposure, the signs of hearing loss, and the latest advancements in hearing care. By maintaining this awareness, you'll be well-equipped to handle any changes in your auditory health.
Next Steps After the Decibel Hearing Test
After completing a decibel hearing test, take the time to discuss the results with your audiologist, determine if any further action is needed, and educate yourself on how to maintain or improve your hearing health. If you have hearing loss, explore the options available to you, such as hearing aids, and embrace the support systems around you. Remember, taking charge of your hearing health can lead to a fuller, more connected life.

Laura Henderson is a health enthusiast and has been interested in healthy and natural methods of eliminating tinnitus and restoring natural hearing for many years.