Reduce Ear Buzzing Using This Method
Concussion Tinnitus: Separating Myths from Facts in Hearing Disorders
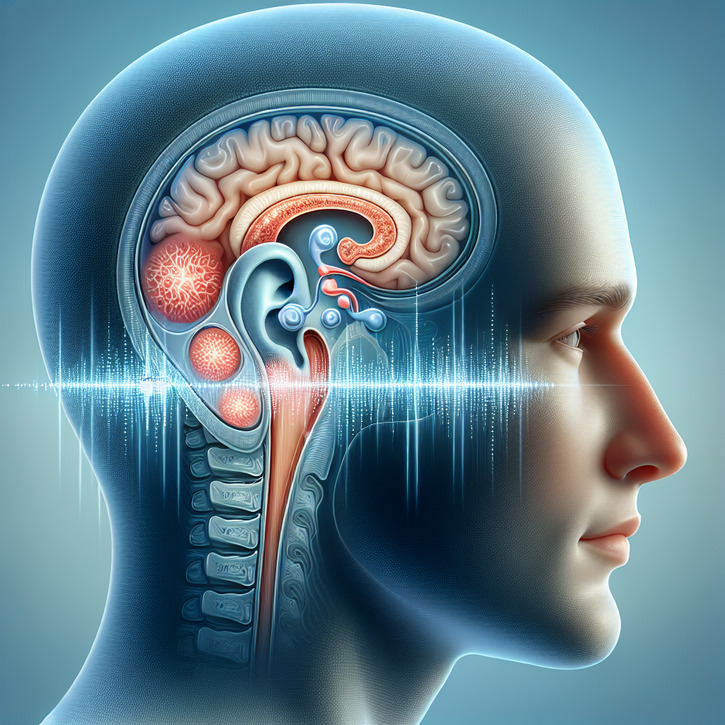
Understanding Concussion Tinnitus: An Introduction
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of concussion tinnitus, a hearing disorder that can emerge following head trauma. Concussion tinnitus refers to the perception of ringing or noise in the ears resulting not from external sounds, but from internal changes within the auditory system after a concussion. With numerous misconceptions circulating, our goal is to provide clarity and evidence-based information to those affected by this condition.
Although the exact prevalence of concussion tinnitus is challenging to quantify, recognizing its symptoms is crucial. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and vary from person to person, making awareness and understanding essential for proper management and support. Through this article, we aim to separate myths from facts, offering a beacon of knowledge for those navigating this complex condition.
The intent of this piece is to act as a reliable resource for individuals experiencing tinnitus after a concussion, as well as their loved ones and healthcare providers. By the end of this read, you'll be equipped with a fact-based understanding of concussion tinnitus, its potential impact, and the pathways available for management and recovery.
This ANCIENT HERB Might Bring Silence To Your Life

Reduce Ear Buzzing Using This Method
Debunking Common Myths Surrounding Concussion Tinnitus
Myth 1: Only Severe Head Injuries Can Cause Tinnitus – It's a common belief that concussion tinnitus only arises from significant head injuries. However, this is not the case. Even mild concussions can disturb the delicate structures of the auditory system, leading to tinnitus. It's essential to monitor for symptoms regardless of the perceived severity of the injury.
Myth 2: Tinnitus Is Always Permanent After a Concussion – Another misconception is that tinnitus, once developed, becomes a lifelong companion. While it can be persistent, many individuals experience a gradual reduction in symptoms over time, and with appropriate interventions, the impact of tinnitus can be significantly managed or even resolved.
Myth 3: Young People Are Less Likely to Experience Concussion Tinnitus – Age does not provide immunity against concussion tinnitus. While the risk of developing chronic tinnitus increases with age, young people are not spared. They can, and do, experience tinnitus following concussive events, emphasizing the need for attention across all age groups.
This ANCIENT HERB Might Bring Silence To Your Life

Reduce Ear Buzzing Using This Pinch Method
The Science Behind Concussion-Induced Tinnitus
Concussions can disrupt the auditory system in several ways. Physical trauma can damage the hair cells within the inner ear that are responsible for translating sound waves into electrical signals, or affect the auditory nerve that carries these signals to the brain. Tinnitus might emerge as the system's response to this alteration in normal function.
The brain's role in tinnitus perception is pivotal. Following a concussion, the brain may interpret the disruption in auditory signaling as sound, leading to the experience of tinnitus. This phenomenon indicates that tinnitus is not solely an ear issue but also involves complex neural pathways.
Research suggests a correlation between concussion severity and the risk of developing tinnitus. More significant head trauma may lead to more pronounced auditory disruptions. However, the relationship is not absolute, and even less severe concussions can result in tinnitus, underscoring the need for individualized assessment and care.
Scientist’s Discovery Quickly Addresses Hearing Loss…

Hundreds of thousands are already using this “weird hack”…
Diagnosing Concussion Tinnitus: What the Process Entails
Diagnosing concussion tinnitus begins with a thorough assessment. A healthcare provider will delve into the patient's medical history, including the details of the injury and the onset of symptoms. This initial conversation is critical for guiding subsequent diagnostic steps and understanding the individual's specific circumstances.
Audiological evaluations are an integral part of the diagnostic process. These may include hearing tests to gauge auditory function and sensitivity, as well as assessments specifically designed to characterize tinnitus. These diagnostic tests help pinpoint the nature and extent of the auditory disruption.
Adopting a multidisciplinary approach is vital when diagnosing and managing concussion tinnitus. Collaboration between audiologists, neurologists, and other specialists can provide a comprehensive understanding of the condition, ensuring that management strategies are tailored to the individual's unique needs and experiences.
Scientist’s Discovery Means a Lot for Hearing Loss…

Thousands of people are already using this “strange hack”…
Treatment Options for Concussion Tinnitus
Managing symptoms may involve the use of hearing aids and sound therapy. Hearing aids can amplify environmental sounds, potentially diminishing the prominence of tinnitus. Sound therapy uses external noises to alter the patient's perception of tinnitus, providing relief and enhancing quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other forms of psychological support have proven effective for many dealing with tinnitus. By addressing the emotional and cognitive responses to tinnitus, CBT can reduce its impact and help individuals develop coping strategies.
Emerging treatments and ongoing research continue to expand the arsenal against concussion tinnitus. Innovative approaches, such as neuromodulation techniques and targeted drug therapies, offer hope for more effective management and potential relief for those affected by this condition.
Try this tonight at home…

Scientists have recently discovered an unusual technique that can reduce tinnitus…
This strange “hearing hack” is so powerful it does not take a lot of time, and works regardless of...
Living with Concussion Tinnitus: Tips and Coping Strategies
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in reducing the impact of tinnitus. Simple changes, like avoiding exposure to loud noises and managing stress levels, can help. Moreover, creating a sound-rich environment, such as using white noise machines, can be beneficial in minimizing the focus on tinnitus.
Support networks and resources are invaluable for individuals with tinnitus. Connecting with others who understand the experience can provide emotional support and practical tips for managing daily life. Professional counseling and support groups can also be instrumental in navigating the challenges of living with tinnitus.
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can offer relief from the constant presence of tinnitus. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help shift focus away from the symptoms, promoting relaxation and potentially easing the perceived intensity of tinnitus.
This Quick Technique is Surprisingly Effective

This quickly applied Technique is Unusually Effective
The Road to Recovery: Rehabilitation and Prognosis
The typical timeline for concussion tinnitus recovery varies widely. Some individuals may notice improvement within weeks, while others may take months or longer. Factors such as the severity of the concussion, the presence of co-occurring conditions, and the effectiveness of treatment can all influence recovery time.
Several factors influence individual prognosis, including age, overall health, and the promptness of treatment initiation. Early intervention can be crucial in managing symptoms and improving outcomes. However, each person's journey with tinnitus is unique, and it's important to maintain realistic expectations while pursuing treatment.
Seeking further medical advice is recommended if symptoms persist or worsen. Additionally, if new symptoms arise, or if there's a significant change in the pattern or intensity of tinnitus, consulting with healthcare providers can ensure that appropriate care is received and any underlying issues are addressed.
Conclusion: Embracing a Fact-Based Understanding of Concussion Tinnitus
We've traversed the landscape of concussion tinnitus, separating persistent myths from the realities backed by science. By understanding the nuances of this condition, individuals affected by tinnitus can make informed decisions about their care.
The importance of ongoing education and awareness cannot be overstated. As our understanding of concussion tinnitus grows, so does our ability to support those living with it. By staying informed, we empower individuals and healthcare professionals alike to confront this challenge with knowledge and compassion.
Encouraging further research and advocacy is essential in advancing the field. Continued exploration into the causes, treatments, and support mechanisms for concussion tinnitus will pave the way for improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected. Together, we can foster a future where the impact of concussion tinnitus is minimized, and the sound of silence is restored.

Laura Henderson is a health enthusiast and has been interested in healthy and natural methods of eliminating tinnitus and restoring natural hearing for many years.




