Reduce Ear Buzzing Using This Method
Breaking Down the Myths: Getting the Facts Straight on Muscular Tinnitus
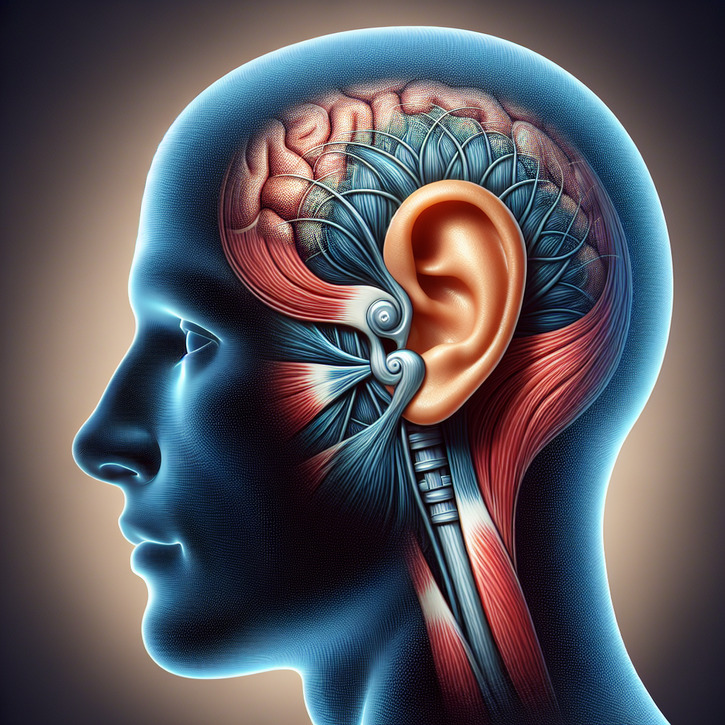
Introduction to Muscular Tinnitus
When we think about tinnitus, the condition that brings persistent ringing or buzzing to one's ears, we often overlook a subtype known as muscular tinnitus. Unlike the more common forms of tinnitus that stem from auditory nerve issues, muscular tinnitus originates from the muscles within the ear. This condition can be just as disruptive, yet is frequently misunderstood. In this blog post, we'll navigate the intricacies of muscular tinnitus, dispel prevalent myths, and provide clarity on this lesser-known auditory disorder.
Understanding the Basics of Muscular Tinnitus
Muscular tinnitus is characterized by sounds that can be heard as clicks or crackling within the ear. These noises are produced by the involuntary contractions of muscles in the middle ear, specifically the tensor tympani and stapedius. Unlike the constant ringing of other tinnitus types, the sounds from muscular tinnitus are usually intermittent and can often be modulated by certain movements, such as jaw clenching or eye movements.
Common Misconceptions About Muscular Tinnitus
There are several misconceptions surrounding muscular tinnitus. Many people believe that this type of tinnitus is extremely rare, always indicates a serious underlying condition, and that there are no effective treatments. These beliefs perpetuate unnecessary anxiety and could deter sufferers from seeking help. This blog aims to correct these falsehoods and present a more accurate picture.
Purpose of the Blog Post
The primary purpose of this post is to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of muscular tinnitus. By exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we aspire to empower those affected with the knowledge to manage their condition effectively. Let's delve into what causes muscular tinnitus and begin to unravel the truth behind the myths.
Scientist’s Discovery Quickly Addresses Hearing Loss…

Hundreds of thousands are already using this “weird hack”…
Exploring the Causes of Muscular Tinnitus
The most direct cause of muscular tinnitus is the dysfunction of the tensor tympani and stapedius muscles. These tiny muscles usually respond reflexively to loud sounds, helping to dampen their impact and protect the inner ear. However, when they contract spasmodically, they can produce the distinctive sounds associated with muscular tinnitus. Understanding the role of these muscles is a significant step in recognizing this condition.
The Role of the Tensor Tympani and Stapedius Muscles
The tensor tympani and stapedius muscles serve as a natural defense mechanism for the inner ear. Their reflexive actions control the tension on the eardrum and the ossicles, which are small bones in the ear that transmit sound. However, when these muscles contract irregularly or excessively, the resulting vibrations can lead to the clicking and popping sounds of muscular tinnitus.
Impact of Stress and Anxiety on Muscular Tinnitus
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate muscular tinnitus. When we experience heightened stress, our body's fight or flight response can trigger muscle tension, including in the muscles within our ears. This increased tension may lead to more frequent or severe episodes of muscular tinnitus, creating a challenging cycle of stress and symptoms.
Dental Issues and Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ)
Dental problems and disorders such as temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) are also potential culprits in the development of muscular tinnitus. Since the muscles involved in tinnitus are closely connected to the jaw, issues with dental health or jaw alignment can directly impact these muscles, leading to the condition. It's essential for individuals with muscular tinnitus to consider a dental evaluation as part of their diagnosis.
This ANCIENT HERB Might Bring Silence To Your Life

Reduce Ear Buzzing Using This Method
Debunking Myths about Muscular Tinnitus
It's time to confront the myths head-on and reveal the truth about muscular tinnitus. These myths can create misconceptions and hinder proper understanding and management of the condition. Let's address and debunk these one by one.
Myth 1: Muscular Tinnitus is Extremely Rare
One common misconception is that muscular tinnitus is an exceedingly rare phenomenon. However, while it may not be as prevalent as other types of tinnitus, it is not exceptionally uncommon. Misdiagnosis or underreporting could be factors contributing to this myth, as many people may not realize that their symptoms are due to muscular tinnitus.
Myth 2: Muscular Tinnitus is Always a Sign of a Serious Condition
Another pervasive myth is that muscular tinnitus is always indicative of a severe health issue. While it's true that it can sometimes signal underlying conditions, many cases of muscular tinnitus are benign and can be effectively managed. It's essential not to jump to conclusions and instead seek a thorough evaluation.
Myth 3: There is No Treatment for Muscular Tinnitus
Perhaps the most discouraging myth is the belief that there is no treatment for muscular tinnitus. This is far from the truth. Various management strategies and treatments can alleviate the symptoms for many individuals. Understanding your options can lead to significant improvements in quality of life.
Scientist’s Discovery Means a Lot for Hearing Loss…

Thousands of people are already using this “strange hack”…
The Symptoms of Muscular Tinnitus
Recognizing the symptoms of muscular tinnitus is vital for diagnosis and treatment. The sounds associated with this condition can range from clicking to a crackling noise and differ significantly from the constant ringing of other tinnitus types. Knowing what to listen for is the first step toward identification.
Understanding the Sound Profile
The sound profile of muscular tinnitus can be quite distinctive. It often presents as rhythmic clicking or a crackling sound that can sometimes be felt as much as heard. These sounds may be sporadic or can occur in a pattern, often triggered by certain movements or actions, such as chewing or yawning.
Recognizing the Patterns of Occurrence
Patterns of occurrence in muscular tinnitus can provide clues to its triggers and causes. Some individuals may notice that their symptoms worsen during periods of stress, after extended jaw use, or when engaging in activities that strain the neck or facial muscles. Tracking these patterns can be helpful in managing the condition.
Connection with Other Ear-Related Symptoms
Muscular tinnitus may also be associated with other ear-related symptoms, such as a sensation of fullness in the ear or a change in hearing sensitivity. These accompanying signs can help differentiate muscular tinnitus from other types and guide the diagnostic process.
Try this tonight at home…

Scientists have recently discovered an unusual technique that can reduce tinnitus…
This strange “hearing hack” is so powerful it does not take a lot of time, and works regardless of...
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Muscular Tinnitus
Diagnosing muscular tinnitus involves a comprehensive approach. It's crucial to differentiate this type from other forms of tinnitus to ensure appropriate treatment. A blend of medical history, physical examination, and possibly further tests will pave the way for an accurate diagnosis.
The Importance of a Thorough Medical History
A thorough medical history is often the cornerstone of diagnosing muscular tinnitus. During consultations, healthcare providers will inquire about the onset, duration, and nature of the symptoms. They may also ask about any history of ear infections, head trauma, or other relevant health issues that could contribute to tinnitus.
Physical Examination and Tests
A physical examination, including an inspection of the ears, throat, and neck, can offer insights into potential causes of muscular tinnitus. Audiological tests may be conducted to assess hearing function, while imaging studies like an MRI or CT scan might be recommended if a structural abnormality is suspected.
Differentiating Muscular Tinnitus from Other Forms
Differentiating muscular tinnitus from other forms is a critical step in the diagnostic process. This distinction is often made based on the sound profile and triggers of the condition. Specific tests, such as tympanometry, can measure the reflexive actions of the ear muscles and help confirm the diagnosis.
This Quick Technique is Surprisingly Effective

This quickly applied Technique is Unusually Effective
Treatment Options for Muscular Tinnitus
While living with muscular tinnitus can be challenging, there is hope in the form of various treatment options. These strategies can be tailored to address the specific causes and symptoms of the condition, offering relief and improved quality of life for sufferers.
Managing Underlying Conditions
One effective approach to treating muscular tinnitus is managing any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms. This may involve treating ear infections, addressing TMJ disorders, or managing stress and anxiety levels. Addressing these root causes can significantly reduce the occurrence of tinnitus symptoms.
Behavioral and Sound Therapies
Behavioral and sound therapies have shown promise in managing muscular tinnitus. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of tinnitus, while sound therapy can provide relief by masking or habituating the ear to the tinnitus sounds.
Medication and Surgical Interventions
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms, particularly if there is a strong stress or anxiety component. Surgical intervention is rare but may be considered if there is a specific structural issue causing the muscular tinnitus, such as a vascular loop pressing on the ear muscles.
This ANCIENT HERB Might Bring Silence To Your Life

Reduce Ear Buzzing Using This Pinch Method
Living with Muscular Tinnitus
Despite the challenges it presents, many people with muscular tinnitus can lead fulfilling lives by implementing certain lifestyle adjustments and seeking appropriate support. Here are some strategies for managing the condition over the long term.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing Symptoms
Making lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing muscular tinnitus symptoms. This may include practicing relaxation techniques, adjusting dietary habits, or incorporating a regular exercise routine to help reduce stress levels. Additionally, avoiding loud noises and using protective hearing equipment can prevent exacerbation of symptoms.
Support Systems and Counseling
Support systems and counseling can be invaluable resources for individuals with muscular tinnitus. Connecting with others who understand the condition can provide emotional support, while professional counseling can offer strategies for coping with the psychological aspects of living with tinnitus.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Developing long-term management strategies for muscular tinnitus is essential. This may involve routine check-ups with an audiologist or ENT specialist, continued use of sound therapy devices, and staying informed about new research and treatments in the field of auditory health.
Conclusion: Empowerment Through Knowledge
As we conclude our exploration of muscular tinnitus, it's clear that empowerment comes through knowledge. Understanding the condition, debunking the myths, and being aware of the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can transform the experience of those affected by this unique form of tinnitus.
Summarizing Key Points
We've learned that muscular tinnitus, while less common than other types of tinnitus, is not exceptionally rare, nor is it always indicative of a severe condition. There are various treatment options available that can provide relief and improve daily living for those who suffer from this condition.
Encouraging Proactive Health Management
Managing muscular tinnitus successfully requires a proactive approach to health. By seeking medical advice, being an advocate for your care, and making lifestyle adjustments, you can mitigate the impact of tinnitus on your life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Resources for Further Information
For those seeking further information on muscular tinnitus, numerous resources are available. Reputable websites, support groups, and healthcare professionals specializing in ear disorders can provide additional guidance. Staying informed is key to managing this condition effectively.

Laura Henderson is a health enthusiast and has been interested in healthy and natural methods of eliminating tinnitus and restoring natural hearing for many years.




